FREE Lesson Plans and Resources for a Unit Study of World War 2
There are abundant resources for studying World War II online. This is a gathering of the resources we used for our study combined created a free home school curriculum. Hands on and interactive we have included links to lesson plans and websites dealing with the war itself, the war in Europe, the war in the Pacific, life on the home front, the holocaust and the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. We have a complete listing of the History Channel Speech Archive's World War II speeches. Other resources include songs of World War II, activities, books, and videos. As a child I loved reading historical fiction from this time period, my daughter follows in my footsteps. She will be providing reviews of books as part of her lessons.
We start our study with a couple of videos honoring veterans of all the wars.
We start our study with a couple of videos honoring veterans of all the wars.
|
Some2Offer has a page of resources for World War 2 (I haven't had a chance to preview all these resources yet but it look great!)
Middle School resources for WW2
The Futile Search for Stability
The peace settlement at the end of World War I left many nations unhappy and border disputes simmering throughout Europe. The League of Nations proved a weak institution. Democracy was widespread, and women in many European countries gained the right to vote. However, economic problems plagued France, Great Britain, and the German Weimar Republic. When Germany declared that it could not continue to pay reparations, France occupied one German region as a source of reparations. An American plan reduced the burden of reparations and led to a period of prosperity and American investment in Europe. The prosperity ended with the economic collapse of 1929 and the Great Depression. European governments tried different approaches to ending the depression. Many middle-class Germans began to identify with antidemocratic political parties. The new American president, Franklin Delano Roosevelt, pursued a policy of active government intervention in the economy that came to be known as the New Deal. YOUTUBE Playlist
The Great Depression VIEWERS DISCRETION ADVISED. imaged from the HOLOCAUST CONCENTRATION CAMPS @ last 2 minutes
The Rise of Dictatorial Regimes
TEXTBOOK Reading By 1939 most European democracies had collapsed. Only France and Great Britain remained democratic. Benito Mussolini began his political career as a Socialist, but he abandoned socialism for fascism, which glorified the state and justified the suppression of all political dissent. In Italy, Mussolini outlawed most political opposition, but also compromised with powerful groups and never achieved totalitarian control. After the Russian civil war, Lenin restored capitalist practices to prevent economic and political collapse. After Lenin's death, Joseph Stalin emerged as the most powerful Communist figure. Stalin eliminated the Bolsheviks of the revolutionary era and established totalitarian rule. His program of rapid industrialization and collectivization forced horrendous sacrifices on the population. His political purges caused millions to be arrested, imprisoned, and executed. Elsewhere in eastern Europe and in Francisco Franco's Spain, authoritarian regimes were mainly concerned with preserving the existing social order. WATCH:
How to implant a dictatorship Fascism, Socialism, Democracy - the differences
Former US President Reagan defines Fascim
Hitler and Nazi Germany AND The Holocaust
Adolf Hitler, a failed student and artist, built up a small racist, anti-Semitic political party in Germany after World War I. Hitler's Beer Hall Putsch failed. In prison, he wrote Mein Kampf-an account of his movement and his views. As democracy broke down, right-wing elites looked to Hitler for leadership. In 1933 Hitler became chancellor. Amid constant chaos and conflict, Hitler used terror and repression to gain totalitarian control. Meanwhile, a massive rearmament program put Germans back to work. Mass demonstrations and spectacles rallied Germans around Hitler's policies, chief among these the belief in "Aryan" (German) superiority. All major institutions were brought under Nazi control. Women's primary role was to bear children and care for the home. Hitler's Nuremberg Laws established official persecution of Jews. A more violent anti-Semitic phase began in 1938 with a destructive rampage against Jews and the deportation of thousands to concentration camps. Increasingly drastic steps barred Jews from attending school, earning a living, or engaging in Nazi society. Middle School
High School
|
Multi MediaThe 20'sPROPAGANDA and Persuasion
support from home...BIOGRAPHIES of Heroes
Righteous Holocaust Rescuers. A collection of 18 brave men, women and children who saved 1000's.
-as collected by a home school teen 
Sir Nicholas Winton saves 669 children During WWII, she got permission to work in the Warsaw ghetto, as a Plumbing/Sewer specialist with an 'ulterior motive' - to smuggle out & save 2500 kids/infants. She was caught & Nazi's broke both her legs, arms & beat her severely. She kept a record of the names of each child in a glass jar, buried under a tree. After the war, she tried to locate parents that may have survived, to reunited the family. She was nominated for the 2007 Nobel Peace Prize. Irena Sendler, Died May 12, 2008 at age 98.
Read about More Heroes during the Holocaust
HolcaustHolocaust Timeline- from Virginia Holocaust Museum Free Study Guide for The Hiding Place by Corrie ten Boom The Hiding Place Study Guide by Progeny Press United States Holocaust Memorial Museum includes Some Where Neighbors, online exhibits, Dictionary |
The Course of World War II
additional assignments:
Watch Battle of Britain (youtube) and Powerpoint , Listen to this news brief after the
Blitz, Listen to one woman’s experience., Listen to Winston Churchill.
Read: from text 329-333, The rise of Hitler,
**optional watch Blitzkrieg**
Write: Worksheet, WRITE a news broadcast about the Blitz (30 seconds) and perform it as if on the radio.
Complete timeline for 1939- 1941
~
German forces swept through northern Europe early in the war and set up the Vichy government in France.
German air attacks on Great Britain resulted in fierce British retaliation. In the east, harsh weather and a resolute Soviet Union defeated an invading German army. The Japanese conquered the Pacific but miscalculated when they attacked the U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor. The United States surprised Japan by abandoning its neutrality and entering the war to retake the Pacific. By the end of 1943, the tide had turned against Germany, Italy, and Japan. After the invasion of Normandy, the Allies liberated Paris and defeated Germany. U.S. president Harry Truman, British prime minister Winston Churchill, and Soviet premier Joseph Stalin met at Potsdam, Germany, to plan the postwar world. The war in Asia continued until the United States dropped atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, causing massive casualties and bringing Japan's surrender.
additional assignments:
Watch Battle of Britain (youtube) and Powerpoint , Listen to this news brief after the
Blitz, Listen to one woman’s experience., Listen to Winston Churchill.
Read: from text 329-333, The rise of Hitler,
**optional watch Blitzkrieg**
Write: Worksheet, WRITE a news broadcast about the Blitz (30 seconds) and perform it as if on the radio.
Complete timeline for 1939- 1941
~
German forces swept through northern Europe early in the war and set up the Vichy government in France.
German air attacks on Great Britain resulted in fierce British retaliation. In the east, harsh weather and a resolute Soviet Union defeated an invading German army. The Japanese conquered the Pacific but miscalculated when they attacked the U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor. The United States surprised Japan by abandoning its neutrality and entering the war to retake the Pacific. By the end of 1943, the tide had turned against Germany, Italy, and Japan. After the invasion of Normandy, the Allies liberated Paris and defeated Germany. U.S. president Harry Truman, British prime minister Winston Churchill, and Soviet premier Joseph Stalin met at Potsdam, Germany, to plan the postwar world. The war in Asia continued until the United States dropped atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, causing massive casualties and bringing Japan's surrender.

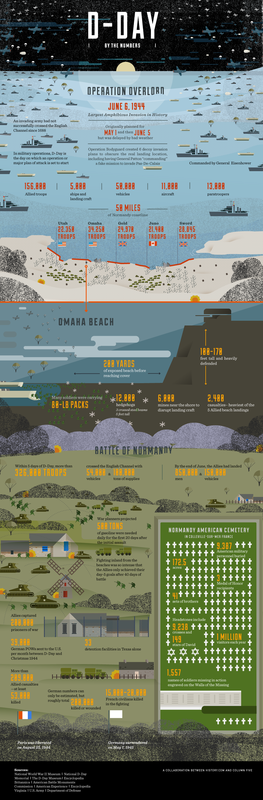
D - DayBritish artist Jamie, accompanied by numerous volunteers, took to the beaches of Normandy with rakes and stencils in hand to etch 9,000 silhouettes representing fallen people into the sand. Titled The Fallen 9000<http://thefallen9000.info/> , the piece is meant as a stark visual reminder of those who died during the D-Day beach landings at Arromanches on June 6th, 1944 during WWII. The original team consisted of 60 volunteers, but as word s pread nearly 500 additional local residents arrived to help with the temporary installation that lasted only a few hours before being washed away by the tide.
9,000 Fallen Soldiers Etched into the Sand on Normandy Beach to Commemorate Peace Day on September 25, 2013 D Day by the Numbers - history.com interactive |